Portulaca
Overview
The Portulaca plant, commonly known as “moss rose” or purslane, is a genus of succulent flowering plants with over 100 species. Well-suited for warm regions, it stands out for its vibrant flowers and resilient nature. Portulaca oleracea, an edible variety, is favored for its nutritional value but can be invasive.
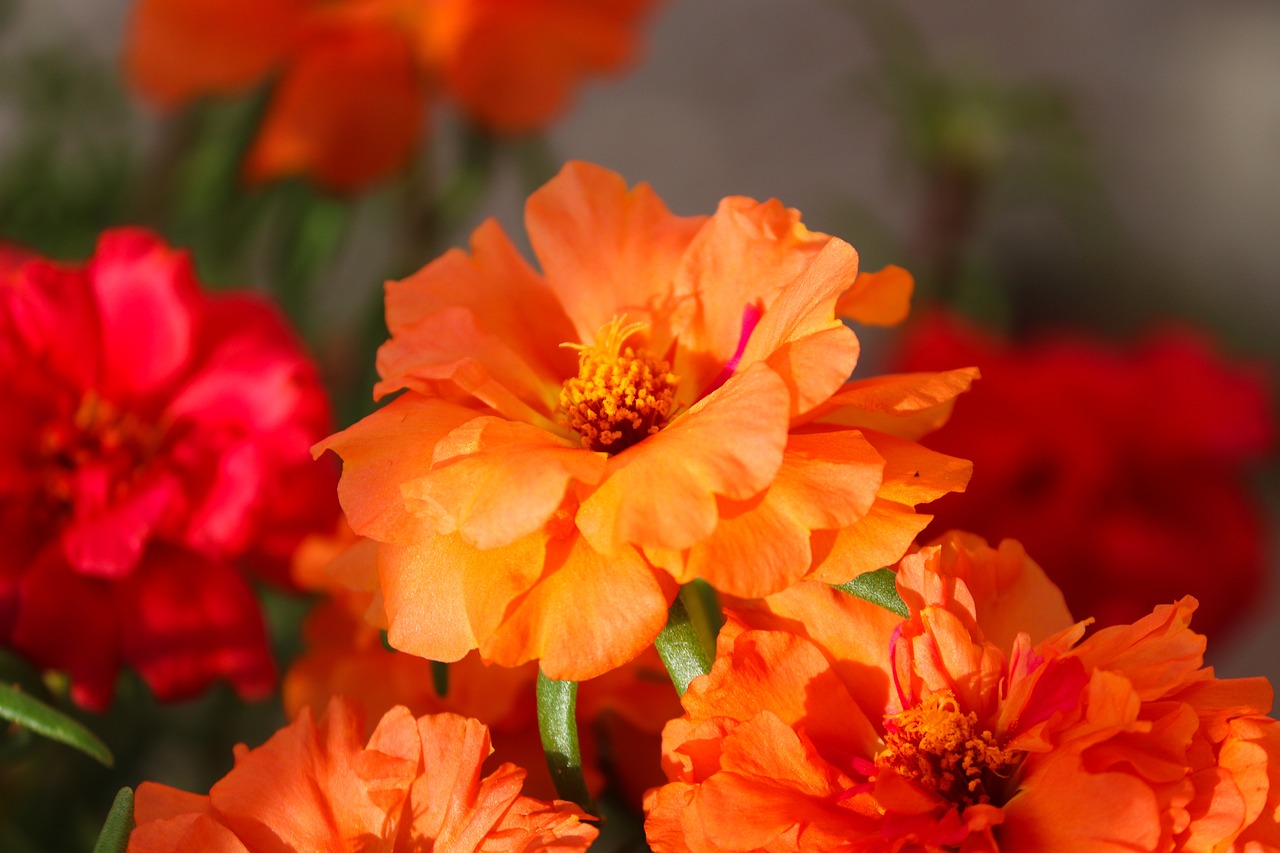

Characteristics
Known for its colorful flowers, succulent leaves, and resilience in full sun and well-drained conditions.
Region
Found in the tropics and warm temperate regions.
Natural Habitat
Typically found in dry, sandy soils and wastelands in warm temperate and tropical regions.
Cultivation
Requires full sun, minimal water, and well-drained soil.
Uses and Benefits
Portulaca plants, specifically the Portulaca oleracea, offer more than just aesthetic value. Recognized for its culinary and ornamental uses, purslane can be a nutritious addition to meals and a vibrant choice for gardens.
- Edible Qualities: The leaves of Portulaca oleracea are packed with nutrients, including omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals3.
- Ornamental Appeal: With their succulent leaves and bright flowers, they are ideal for adding color to landscapes and containers1 2.
- Drought Resistance: As hardy succulents, portulaca plants require minimal water, making them perfect for xeriscaping2.
- Easy Cultivation: They can thrive in poor, well-drained soils and still produce a bounty of flowers, reducing the need for fertilizers2.
Whether you’re garnishing a dish or brightening your garden, Portulaca oleracea is a versatile plant that provides both beauty and utility.

Cultivation Tips
Cultivating Portulaca plants can be a rewarding endeavor for those who love vibrant and low-maintenance gardens. Follow a few essential tips to ensure your Portulaca, or ‘moss rose’, thrives:
- Sow seeds on the soil surface after the last frost, ensuring they are spaced 4 to 24 inches apart for adequate room to grow4.
- In full sun, Portulaca plants will flourish, so pick a spot that receives plenty of daylight2.
- These plants prefer well-drained soil—be wary of overwatering to prevent root rot2.
- If starting seeds indoors, mix them with a growing medium and place them in a freezer bag to maintain moisture. Then, refrigerate for 2-3 weeks for stratification4.
- Use peat pots to help germination. Expect sprouts within one to three weeks, provided they have sufficient light4.
Understanding Portulaca‘s growing conditions can make a significant difference in their success. These plants are drought-tolerant – a heaven-sent trait for the forgetful waterer – and their stunning flowers make them a notable addition to any garden. Keep in mind, in some areas, Portulaca oleracea
Seasonal Considerations
When planning your garden with the vibrant Portulaca herb, consider the following seasonal tips:
- Spring: Stock up on Portulaca from nurseries at the start of spring1.
- Summer: Maintain its vibrant colors by ensuring it receives ample sunlight.
- Fall: Enjoy the plant’s resilience as it continues to display its beauty through the autumn months1.
- Winter: In cold climates, Portulaca may not survive outdoors; consider moving indoor or collecting seeds for the next season.
For best growth, remember to plant after the last frost and situate in well-drained soil in a location that receives full sun.

Issues and Troubleshooting
While Portulaca plants are known for their robust nature, they do encounter a few issues such as overwatering, which can lead to root rot. It’s vital to ensure that soil is well-draining to prevent this problem.
Insect pests like aphids and mealybugs can also pose a threat. These can be managed by regular inspection and, if needed, the use of insecticidal soap or neem oil.
Lastly, although Portulaca is heat-tolerant, extreme heat can stress the plant, causing leaf drop. Ensure adequate water during intensely hot periods, but be careful not to overwater2 4.
For optimal health, keep an eye on the moisture level of the soil and inspect your plants regularly for pests.
History and Folklore
Portulaca, known as “moss rose,” holds rich history and folklore. While specific stories are sparse, vegetation like Portulaca oleracea, also called purslane, has been recognized for centuries. Revered in various cultures for its resilience and hardy nature, purslane’s succulent leaves and colorful blooms are worldwide symbols of perseverance and beauty. In some traditions, purslane was thought to protect against evil spirits, reflecting its tenacity. More than just a folktale plant, purslane has been utilized across history in culinary and medicinal contexts, further intertwining its legacy with human life.
References
1. Garden Beast, “Portulaca Plant Guide: How to Plant & Care for ‘Moss Rose’”, https://gardenbeast.com/portulaca-guide/
2. North Carolina Extension Gardener Plant Toolbox, “Portulaca”, https://plants.ces.ncsu.edu/plants/portulaca/
3. Wikipedia, “Portulaca”, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portulaca
4. Gardeners HQ, “Portulaca Plant Growing & Care Guide for Gardeners”, https://www.gardenershq.com/Portulaca-Purslane.php
5. CABI Compendium, “Portulaca oleracea (purslane)”, https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/10.1079/cabicompendium.43609
Image Credit: manfredrichter
Image Credit: manfredrichter
Image Credit: WikimediaImages
Nicolas Duval
Nicolas is a passionate advocate for nature and the art of wildcrafting. His dedication shines through in Wildcraftia, a website he meticulously crafted to serve as a haven for nature enthusiasts worldwide. Driven by a deep appreciation for nature’s connection to humanity, Nicolas embarked on his journey in 2011 with SmokableHerbs, a platform showcasing his love for nature’s bounty. Building upon this foundation, he established Smokably, a thriving online store offering premium herbs and blends to a global audience.