Mopane
Overview
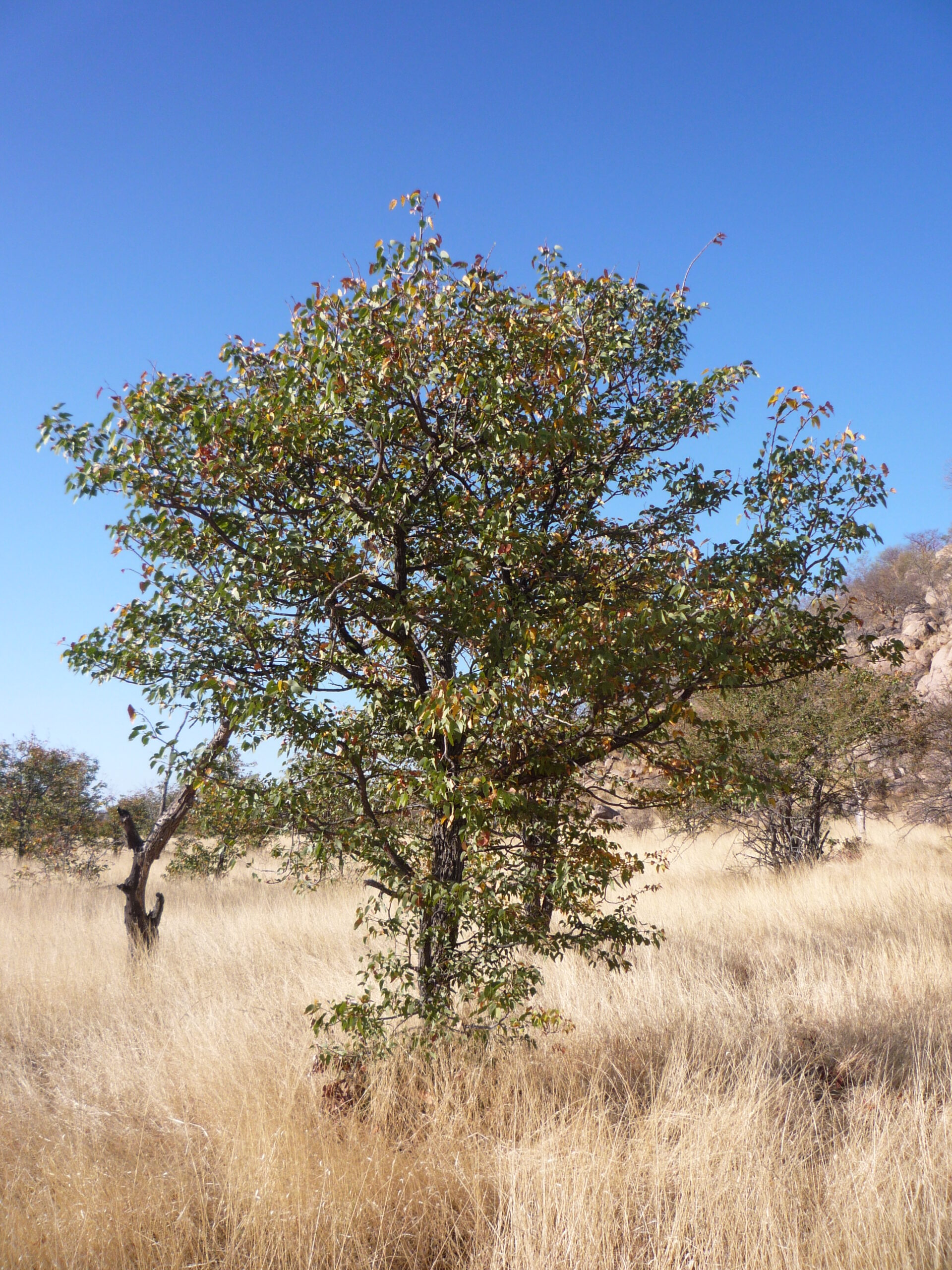
The Mopane plant, or Colophospermum mopane, is a legume-family tree known for its butterfly-shaped leaves and grows predominantly in Sub-Sahara Africa. Thriving in hot, dry climates, it varies in form from a shrub to a tall tree and can reach up to 10 meters with a V-shaped crown. Despite limited information on its uses, Mopane is notable for its essential oil-producing seeds and robust wood with antibacterial qualities1 2 3 4.

Characteristics
Known for its butterfly-shaped leaves, iron-hard wood, and dominance in hot, dry Sub-Saharan environments.
Region
The Mopane plant is typically found in hot, dry, low-lying areas of Sub-Saharan Africa.
Natural Habitat
The Mopane plant is typically found in hot, dry, low-lying areas and woodlands in Sub-Saharan Africa.
Cultivation
Prefers full sun, tolerant to drought, and requires well-drained soils with a preference for alkaline to neutral conditions.
Uses and Benefits
The Mopane plant offers a range of unique uses and benefits that extend beyond its resilience in hot and arid conditions. While not widely recognized for culinary or medicinal purposes, the tree’s seeds carry a distinctive pine-like aroma and contribute to Namibia’s essential oil production 3.
Mopane wood is highly valued for its exceptional strength and bacteria-killing properties, making it a prized resource in its native regions 2. Some notable uses of Mopane wood include:
- Construction: The durable wood is used for building homes, fences, and other structures.
- Firewood: Mopane wood burns slowly and produces high-quality, long-lasting coals.
- Crafts: Artisans create beautiful carvings, furniture, and tools from the dense wood.
In addition to its practical applications, the Mopane tree plays a vital role in supporting the biodiversity of Sub-Saharan landscapes. Its presence helps to:
- Provide habitat and food for various wildlife species
- Prevent soil erosion and maintain ecosystem balance
- Serve as a natural windbreak and shade source in arid regions
The Mopane plant’s quiet but significant contributions to its native environment showcase the inherent value of indigenous flora. By understanding and appreciating the unique uses and benefits of plants like Colophospermum mopane, we can better support the conservation and sustainable use of these valuable natural resources.

Cultivation Tips
When cultivating the hardy Mopane tree (Colophospermum mopane), it’s important to remember that it thrives in hot, arid conditions, similar to its native Sub-Saharan African habitat4. This resilient tree prefers elevations between 200 and 1,150 meters and can grow as either a robust shrub or a statuesque tree with a distinctive V-shaped crown2.
Mopane is known for its ability to rebound after adversity, as it can easily coppice and send up multiple stems1. Some key cultivation tips include:
- Provide well-draining soil and full sun exposure
- Water deeply but infrequently, allowing the soil to dry between watering
- Protect young plants from extreme cold and frost
- Prune to maintain desired shape and size
While Mopane can be slow to produce seeds until it reaches a certain size, patient cultivation is rewarded with a durable plant that produces aromatic seeds5. Young Mopane trees demonstrate a tenacious grip on life, as they are not significantly threatened by fires or grazing5.
With proper care and attention, home gardeners can successfully cultivate this fascinating and resilient tree, enjoying its unique characteristics and the satisfaction of nurturing a piece of Sub-Saharan Africa in their own backyard.
Seasonal Considerations
When cultivating the hardy Mopane tree (Colophospermum mopane), it’s important to keep in mind its seasonal preferences. This resilient tree thrives in the hot, arid conditions of its native Sub-Saharan Africa, where it’s right at home under the sun-drenched skies4. To ensure optimal growth, consider the following seasonal factors:
- Elevation: Mopane prefers elevations between 200 and 1,150 meters, where it can form a commanding presence as either a robust shrub or a statuesque tree with a trim V-shaped crown2.
- Resilience: Mopane is no stranger to rebounding after adversity, as it can easily coppice and send up multiple stems1. This adaptability allows it to thrive in challenging environments.
- Seed production: While Mopane can be slow to produce seeds until it reaches a certain stature, patient cultivation is rewarded with a plant known for its durability and the aromatic seeds it produces5.
- Growth cycle: Although Mopane’s growth cycle sometimes faces population bottlenecks, fires and grazing don’t pose a significant threat to its young5, demonstrating its tenacious grip on life no matter the challenges it faces.
By considering these seasonal factors and providing the appropriate care, you can successfully cultivate the Mopane tree and enjoy its unique characteristics in your garden or wildcrafting endeavors.

Issues and Troubleshooting
The Mopane tree, which thrives in the warm and arid regions of Sub-Saharan Africa, faces a unique set of challenges during its growth cycle. Population bottlenecks can arise5, impacting the distribution and abundance of these trees.
Though the Mopane can withstand fire and herbivory to a degree, these events can lead to modifications in the plant’s structure5. Despite these issues, the Mopane is noted for its resilience, with young trees having the ability to coppice, allowing them to recover from damage1. This means that even if the plant’s architecture is altered, its ability to survive remains largely unaffected, showcasing the Mopane’s impressive adaptability to its environment.
To troubleshoot issues with Mopane trees:
- Monitor for signs of stress, such as yellowing leaves or stunted growth
- Ensure the tree receives adequate water during dry spells
- Protect young trees from excessive herbivory using physical barriers or repellents
- If fire damage occurs, allow the tree to coppice and regrow naturally
- Prune damaged or diseased branches to maintain the tree’s health and structure
By understanding the Mopane’s unique challenges and implementing these troubleshooting techniques, nature-conscious individuals can help support the resilience and adaptability of this remarkable tree.
History and Folklore
The Mopane tree, known scientifically as Colophospermum mopane, has a name that is deeply rooted in the local dialects of the regions where it thrives4. This resilient and distinctive tree is an integral part of the Sub-Saharan landscape, intertwining both ecological and cultural significance.
The Mopane’s unique butterfly-shaped leaves and dense, iron-like wood have fueled countless tales and traditions among indigenous communities throughout history. Its presence is a testament to the enduring story of the land it flourishes in, with many legends and historical uses waiting to be uncovered.
Some key points about the Mopane tree’s history and folklore:
- The tree’s name is derived from local dialects, showcasing its deep connection to the people of the region
- Its distinctive appearance has made it a recognizable icon of the Sub-Saharan landscape
- Indigenous communities have developed tales and traditions around the Mopane tree, emphasizing its cultural significance
- The Mopane’s resilience and unique properties have likely contributed to its role in local folklore
While many specific legends and historical uses of the Mopane tree remain a mystery, its enduring presence in the landscape and cultural narratives of Sub-Saharan Africa highlights the intricate relationship between nature and human history.
References
1. Mopane – Whole Earth Education, https://wholeeartheducation.com/mopane/
2. Mopane – Fascinating Africa, https://fascinatingafrica.com/species/mopane/
3. The Mopane Tree – Fantastic Wildlife, https://fantasticwildlife.com/the-mopane-tree/
4. Mopane – Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mopane
5. What shapes the range edge of a dominant African savanna tree, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8093671/
Image Credit: james.harris.anderson Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License
Image Credit: Jose Carlos Babo Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs License
Image Credit: Hans Hillewaert Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs License
Nicolas Duval
Nicolas is a passionate advocate for nature and the art of wildcrafting. His dedication shines through in Wildcraftia, a website he meticulously crafted to serve as a haven for nature enthusiasts worldwide. Driven by a deep appreciation for nature’s connection to humanity, Nicolas embarked on his journey in 2011 with SmokableHerbs, a platform showcasing his love for nature’s bounty. Building upon this foundation, he established Smokably, a thriving online store offering premium herbs and blends to a global audience.