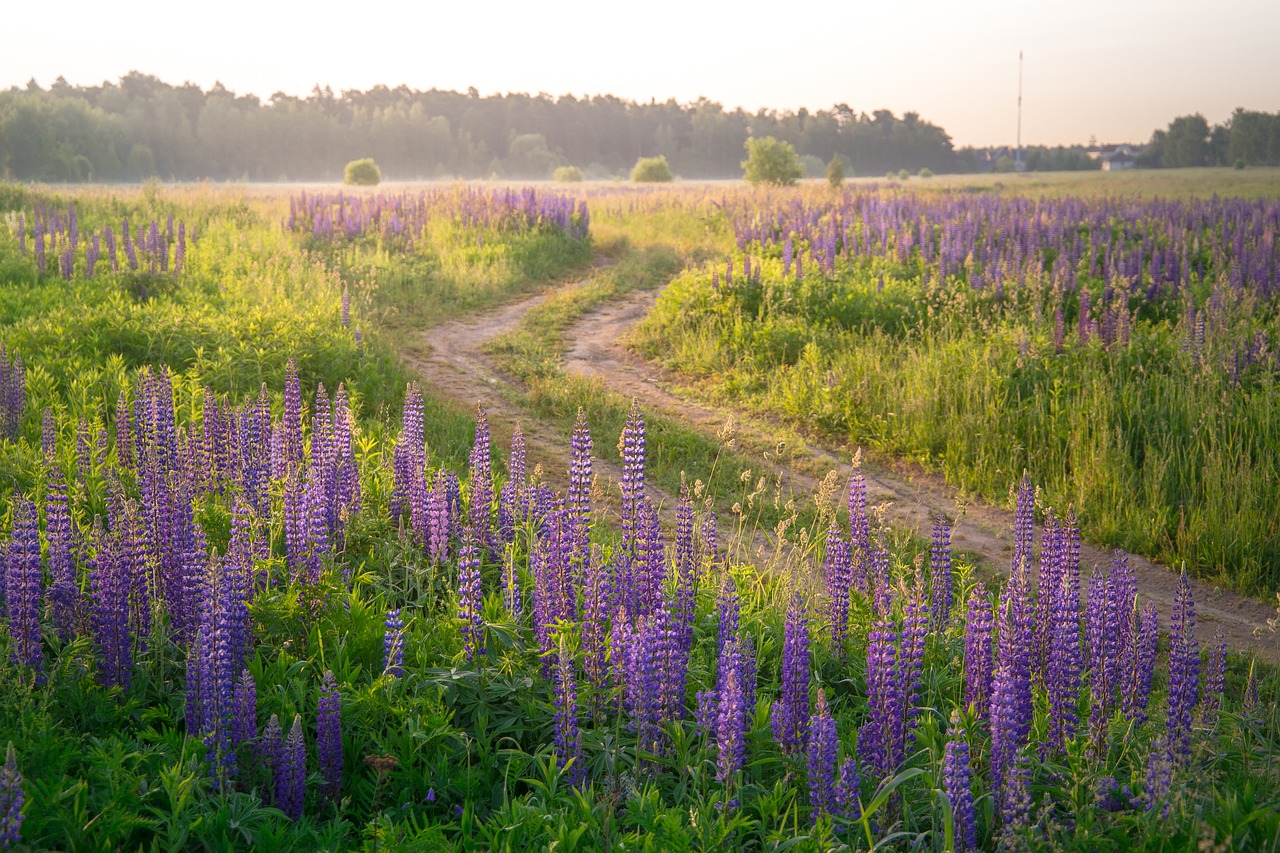
Lupine
Overview
The Lupinus herb, part of the Fabaceae family, is celebrated for its brilliant flower spikes. Flourishing in cooler regions, Lupines require full sun and acidic soil, bringing pollinators and color to gardens while being resistant to deer. They offer ease of maintenance, suiting various landscapes, and bloom in late spring to early summer.

Characteristics
Known for vibrant flower spikes, pollinator-friendliness, and deer resistance.
Region
Northern climates with cooler summers and northern United States, southern Canada, Pacific Northwest, West Coast, and New England; also as annuals in the deep South’s regions (Zones 7-9).
Natural Habitat
Lupines are commonly found in wild meadows and along roadsides.
Cultivation
Thrives in full sun (at least 6 hours daily), requires weekly watering, and prefers acidic soil.
Uses and Benefits
Lupines, known for their striking spikes of colorful flowers, offer a range of uses and benefits in the garden and beyond. These hardy perennials are loved for their:
- Attractiveness to beneficial pollinators like bees and butterflies, helping to support local ecosystems.
- Resistance to deer, which protects other garden plants and maintains the visual appeal of your outdoor space.
- Compatibility with xeric gardening, as they are well-suited to water-conserving landscapes.
- Easy integration into native landscaping, enhancing biodiversity.
Additionally, their low-maintenance requirements make lupines a favorite among gardeners looking to create sustainable and vibrant gardens. With hues ranging from deep blues to soft pinks, they are a visual delight and an asset to any gardeners looking to enhance their home’s natural beauty3 4.

Cultivation Tips
To ensure your Lupine plants (genus Lupinus) flourish, consider the following cultivation tips:
- Seed Preparation: Soak Lupine seeds in water until they begin to swell. For those that prefer not to scarify the seeds, a 24-hour soak can serve as an effective alternative.
- Sowing Depth: Plant the seeds at least ½ inch beneath the soil surface to provide the necessary darkness for germination.
- Optimal Soil Temperature: Aim for a soil temperature range between 55 and 60 degrees Fahrenheit to encourage seed germination.
- Site Selection: Choose a location where plants will receive full sunlight for a minimum of 6 hours daily.
- Soil Requirements: Lupines favor acidic soil and require consistent moisture. Weekly watering is typically sufficient.
- Seasonal Timing: Plant your Lupines in the spring or fall, depending on your local climate and the specific Lupine variety.
Regularly tending to these needs will lead to vibrant Lupine blooms enjoyed by pollinators and admired for their deer-resistant qualities1 2 3 5.
Seasonal Considerations
For those who are incorporating the lovely Lupinus into their garden, here are some important seasonal considerations to ensure these vibrant bloomers thrive:
- Plant Lupinus seeds or seedlings either in spring or fall for best results3.
- The blooming period varies, but generally extends from late spring to early July. This is when you can expect to see their beautiful flower spikes4.
- In northern areas with cooler summers, Lupinus plants prefer full sunlight, with at least 6 hours per day1.
- In warmer regions, such as Zones 7-9, consider planting Lupinus as annuals to mitigate the stress of heat and humidity2.
Proper timing and seasonal adjustment can yield a stunning display of color and contribute to a thriving garden habitat that supports local pollinators.

Issues and Troubleshooting
Common Issues with Lupine Plants
Lupines are robust, but they can struggle in extreme conditions. High heat and humidity, especially in Zones 7-9, can harm these plants2. If your Lupines are showing signs of distress, consider adjusting their environment. Ensure they receive plenty of sunlight—around 6 hours daily—but protect them during the hottest part of the day with partial shade. Avoid overwatering as Lupines dislike soggy roots; aim for moist, well-drained soil. Acidic soil is preferred, so test your soil’s pH and amend it if necessary1. Regular watering is vital, but always confirm the top inch of soil is dry before adding more water. If foliage begins to yellow or droop, reassess your watering schedule and sun exposure, making adjustments as needed to provide optimal growing conditions for your Lupine plants.
History and Folklore
Tracing its roots, many Lupine species hail from North America, suggesting an integral role within the continent’s ecosystems for centuries3. Historically, Lupines have often been associated with transformation and innovation. In ancient tales, Lupines are sometimes cast as a source of protection, repelling malevolent spirits with their radiant blossoms. As a symbol of imagination and creativity, the vibrant spikes of Lupine flowers have inspired countless artists and storytellers. In folklore, Lupines are sometimes thought to possess the power to nourish the soil, interlinking their presence with the natural cycle of life and the nurturing of the earth.
References
1. “How to Grow and Care for Lupine (Bluebonnet) – The Spruce”, https://www.thespruce.com/growing-lupine-flowers-1316034
2. “How to Plant and Grow Lupine – Better Homes & Gardens”, https://www.bhg.com/gardening/plant-dictionary/perennial/lupine/
3. “Growing and Caring for Lupine (Bluebonnet) | The Old Farmer’s Almanac”, https://www.almanac.com/plant/lupines
4. “Complete Guide to Plant, Grow and Care for Lupine Flowers – Planet Natural”, https://www.planetnatural.com/growing-lupine/
5. “How to Plant, Grow and Care For Lupine Flowers – Epic Gardening”, https://www.epicgardening.com/lupine/
Image Credit: mystraysoul
Image Credit: moshehar
Image Credit: 165106
Nicolas Duval
Nicolas is a passionate advocate for nature and the art of wildcrafting. His dedication shines through in Wildcraftia, a website he meticulously crafted to serve as a haven for nature enthusiasts worldwide. Driven by a deep appreciation for nature’s connection to humanity, Nicolas embarked on his journey in 2011 with SmokableHerbs, a platform showcasing his love for nature’s bounty. Building upon this foundation, he established Smokably, a thriving online store offering premium herbs and blends to a global audience.