Lime
Overview
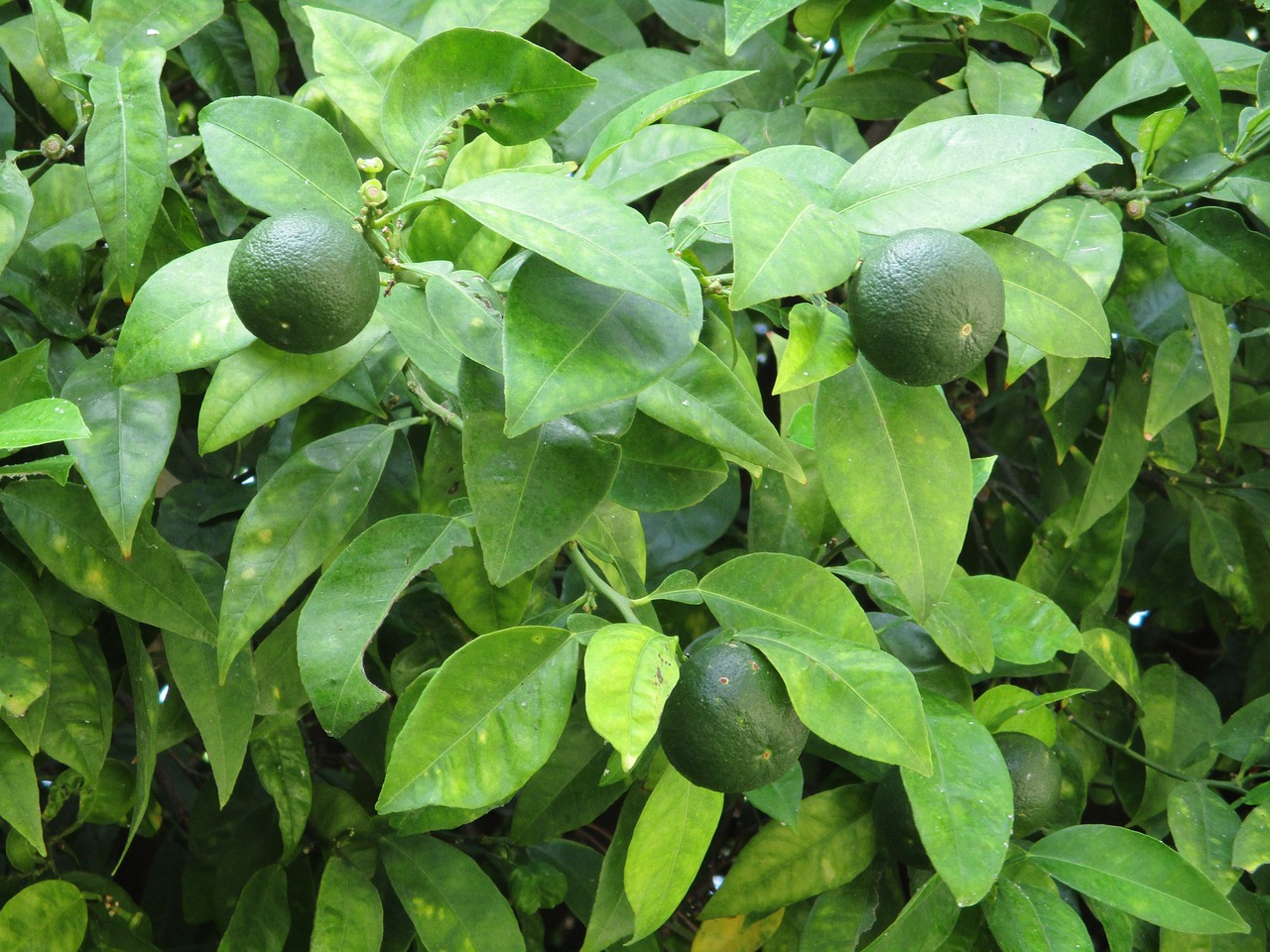
The Lime tree (Citrus aurantifolia) is a versatile plant with oval, thick leaves and is well-known for its aromatic, tangy fruit. Favoring sunny climates for optimal growth, lime trees are easy to care for once properly situated. Persian and key limes are popular for their uses in culinary delights and pickling, with the former recognized for its broad leaves and the latter for its orange-like foliage1 3.

Characteristics
Known for its oval-shaped, thick green leaves, various culinary uses, its requirement for sunny climates, and minimal care post-establishment.
Region
Lime trees are typically grown in tropical and subtropical regions around the world.
Natural Habitat
Lime trees are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions.
Cultivation
Lime trees require full sunlight, moderate watering, and well-drained, fertile soil with a neutral to slightly acidic pH.
Uses and Benefits
The versatile lime, with its invigorating citrus tang, offers a wide range of uses and benefits that extend far beyond its role as a classic beverage garnish. This small but mighty fruit, typically measuring 3 to 4 cm in diameter, is a staple in kitchens around the globe due to its ability to elevate and enhance various dishes and products.
Limes are prized for their distinct sweet and sour flavor profile, which adds a lively kick to an array of culinary delights, including:
- Zesty pickles
- Tantalizing sauces and marinades
- Refreshing salad dressings
- Flavorful curries and stir-fries
Two popular lime varieties, Persian and Key limes, are easily recognizable by their oval shape and greenish-yellow peel when ripe and ready for harvest3.
Beyond its culinary prowess, the lime also boasts an impressive nutritional profile. This citrus fruit is an excellent source of vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant that supports immune function, skin health, and the body’s ability to absorb iron from plant-based sources. By incorporating limes into your diet, you can enjoy a delightful burst of flavor while simultaneously reaping the wellness benefits they offer.
For those with a green thumb, planting a lime tree can be a rewarding and joyful experience. These trees thrive under the sun’s generous rays, making them well-suited for gardens in warm, sunny climates. With proper care and attention, a lime tree can yield a bountiful harvest of sweet and tangy fruits, providing you with a fresh supply of this versatile ingredient right at your fingertips.

Cultivation Tips
Cultivating your own lime tree can provide a delightful and aromatic addition to both your garden and culinary pursuits. When planting, select a location that receives ample sunlight, as these trees thrive in bright, sunny spots. To ensure your lime tree establishes itself well, dig a hole that is wide enough to comfortably fit the roots, but avoid planting too deeply – the depth of the hole should be equal to the size of the rootball.2
Once your lime tree is settled in its new home, you’ll find that it is relatively low-maintenance. Citrus aurantifolia, particularly the resilient Persian lime variety, is quite forgiving and will flourish with minimal attention, provided its basic requirements are met.2 However, it’s essential to keep in mind that lime trees prefer warm temperatures and may require additional protection during colder months if you reside in a cooler climate.
To ensure your lime tree thrives, consider the following care tips:
- Water regularly, especially during dry spells, but avoid overwatering as this can lead to root rot.
- Fertilize your tree with a citrus-specific fertilizer to provide the necessary nutrients for optimal growth and fruit production.
- Prune your lime tree annually to maintain its shape, remove dead or diseased branches, and promote healthy growth.
- Monitor your tree for signs of pests or diseases, and take appropriate action if necessary.
By providing your lime tree with the proper care and attention, you’ll be rewarded with a bountiful harvest of fragrant, zesty limes that will add a burst of flavor to your favorite dishes and beverages.
Seasonal Considerations
When planning your lime tree’s home, consider its seasonal needs. In warm, sunny regions, your lime will happily grow outdoors year-round, thriving in the golden rays. However, if your area is prone to chilly winters, you’ll want to give your lime some extra TLC. Plant it in a sturdy container that can be whisked indoors when the mercury drops, ensuring its delicate leaves and ripening fruits are shielded from the cold.
As the seasons shift, so too will your lime’s care routine. In spring and summer, it will crave consistent moisture, so ensure the soil remains damp but not soggy. A deep drink once or twice a week should suffice, but during particularly hot and dry spells, you may need to water more frequently. Keep an eye on the leaves – if they start to droop or curl, it’s a sign your lime is parched.
Autumn is the time to start preparing your lime for its winter rest. If you’re in a cooler climate, gradually acclimate it to indoor conditions by placing it in a shaded spot outdoors for a week or two before bringing it inside. Once indoors, position it in a bright, sunny window and reduce watering, allowing the soil to dry out slightly between drinks.
As winter melts into spring, it’s time to wake your lime from its slumber. Slowly reintroduce it to the outdoors, placing it in a shaded area for a few hours each day before gradually exposing it to more sunlight. By summer, it should be back in its prime spot, basking in the warm rays and rewarding you with a fragrant, bountiful harvest.
With a little seasonal savvy, your lime tree will thrive, its glossy leaves and tangy fruits a testament to your green thumb. Whether you’re in a balmy paradise or a chillier corner of the world, your lime will adapt and flourish under your watchful care.

Issues and Troubleshooting
Lime trees, cherished for their zest and fragrance, sometimes face a few hiccups. One common issue is overwatering, which can lead to yellowing leaves and root rot. To avoid this problem, ensure your lime tree has adequate drainage and practice moderation in watering.
Pests can also be bothersome for lime trees. Two common culprits are:
- Citrus leaf miners
- Aphids
These pests love to feast on the leaves of lime trees. To manage these critters, you can use gentle pesticides or introduce natural predators like ladybugs to your garden.2
Another issue lime trees may face is nutrient deficiencies, particularly of nitrogen. Signs of a deficiency include:
- Poor growth
- Leaf discoloration
To remedy this, regularly apply a citrus-specific fertilizer to provide your lime tree with the nutrients it needs to thrive.2
Despite these challenges, with a little care and vigilance, your lime tree can be a source of delight and vibrant fruitfulness. By staying attuned to your tree’s needs and addressing issues promptly, you’ll be able to enjoy the refreshing taste of homegrown limes for years to come.
History and Folklore
Steeped in history and cultural significance, the Lime tree (Citrus aurantifolia) has captivated people for centuries. Beyond its tart, refreshing fruit, the Lime tree has played a vital role in the economies of various regions3.
Folklore and traditions have long associated limes with healing, cleansing, and protection. While the specific details of Lime tree myths and stories may have been lost to time, the fruit itself has earned a special place in culinary, medicinal, and even magical realms.
Some of the ways limes have been used throughout history include:
- Culinary: Adding zest and tang to dishes, beverages, and preserves
- Medicinal: Treating scurvy, aiding digestion, and promoting overall health
- Magical: Incorporated into rituals for purification, protection, and blessings
The Lime tree’s enveloping citrusy scent and vibrant fruit continue to evoke a sense of freshness, vitality, and mystery – a testament to its enduring allure and significance in our lives.
References
1. Lime tree: types, harvesting, & characteristics – Plantura, https://www.plantura.garden/uk/fruits/lime-tree/lime-tree-overview
2. How to Grow and Care for a Lime Tree – The Spruce, https://www.thespruce.com/lime-tree-care-guide-7554268
3. Lime | Description, Fruit, Types, Varieties, History, & Facts, https://www.britannica.com/plant/lime
Image Credit: annawaldl
Image Credit: balouriarajesh
Image Credit: ignartonosbg
Nicolas Duval
Nicolas is a passionate advocate for nature and the art of wildcrafting. His dedication shines through in Wildcraftia, a website he meticulously crafted to serve as a haven for nature enthusiasts worldwide. Driven by a deep appreciation for nature’s connection to humanity, Nicolas embarked on his journey in 2011 with SmokableHerbs, a platform showcasing his love for nature’s bounty. Building upon this foundation, he established Smokably, a thriving online store offering premium herbs and blends to a global audience.