Hosta
Overview
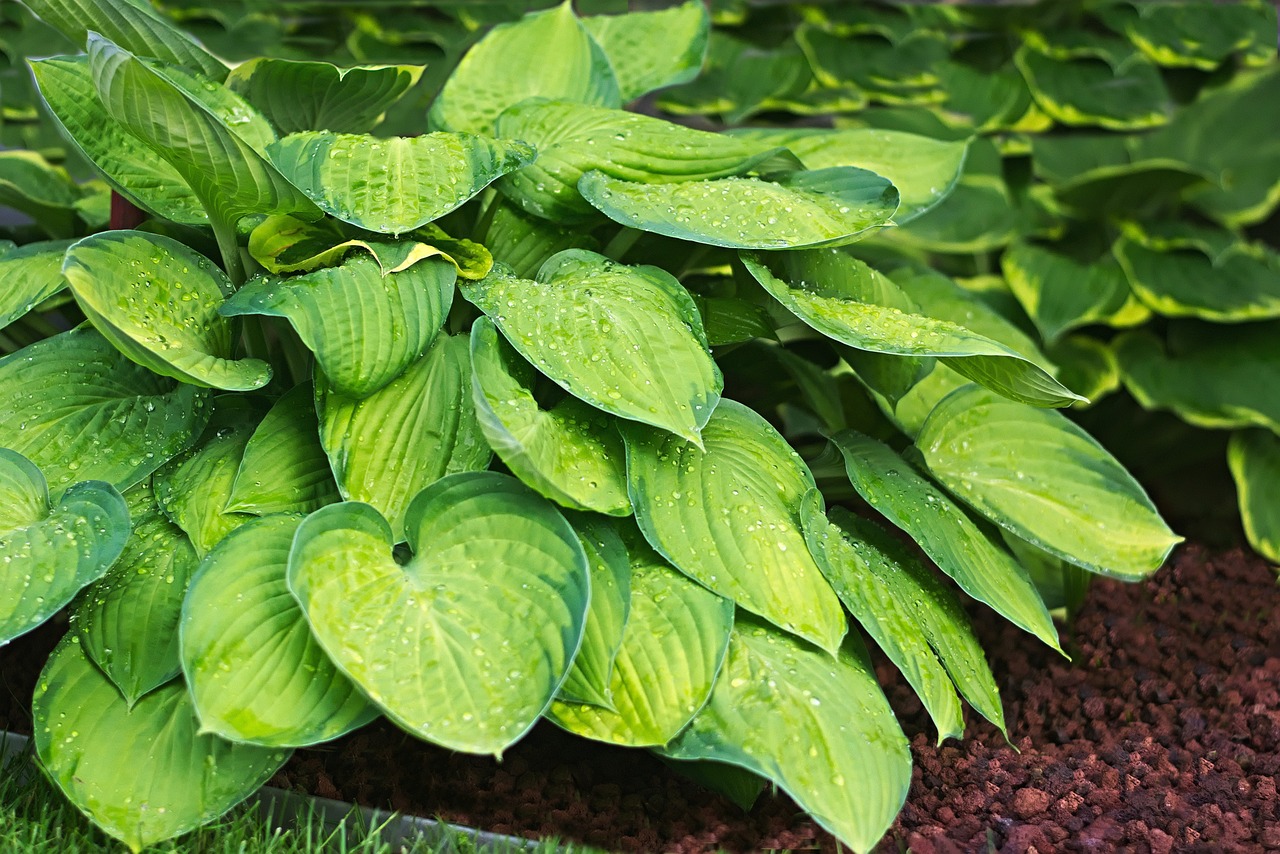
Hostas, the elegant shade dwellers, enhance gardens with their lush foliage. Also called plantain lilies, these members of the Asparagaceae family showcase a tapestry of colors and leaf variegations. Ideal in cooler, shady spots, these low-maintenance, ornamental perennials also present subtle blooms, adding a charming effect to tranquil garden spaces.

Characteristics
Known for its lush foliage, shade tolerance, and variety in size and color.
Region
Hosta plants are commonly grown in temperate regions and are native to Northeast Asia.
Natural Habitat
Hosta plants are commonly found in woodlands, riverbanks, and grassy areas in East Asia.
Cultivation
Prefers partial to full shade, requires consistently moist soil, and thrives in fertile, well-draining soil.
Uses and Benefits
Hostas, with their striking foliage, are a standout feature in any shade garden. These versatile plants offer several benefits:
- They provide an array of shapes and sizes, ideal for ground cover and filling in landscape gaps2.
- Variegated leaves bring contrast and visual appeal to garden designs5.
- Although mainly grown for their leaves, some Hosta varieties produce fragrant flowers that can be a delightful bonus5.
- Their resilience against summer heat and mild droughts makes them a practical choice for a low-maintenance garden1.
Not only do Hostas offer aesthetic value, but their ability to flourish in less sunny corners allows gardeners to brighten up potentially neglected parts of their outdoor space.

Cultivation Tips
Cultivating a thriving Hosta garden starts with understanding these elegant plants’ preferred conditions. Here are some tips to help you grow healthy Hostas:
- Shade is essential: Hostas flourish in partial to full shade. Avoid placing them in areas with intense afternoon sun, as it can scorch their leaves1.
- Soil quality matters: Fertile, well-drained soil enriched with compost or rotted manure will support vigorous growth1.
- Watering needs: While Hostas can tolerate mild drought, consistent moisture helps maintain their lush appearance, especially in warmer months.
- Mulching benefits: Apply a layer of well-rotted manure, compost, or leaf mould annually to conserve moisture and add nutrients to the soil3.
- Division for health: Over time, clumps may become crowded. Divide your Hostas every three to five years to encourage rejuvenation and increase your collection3.
- Watch for pests: Slugs and snails are common culprits that can damage Hostas. Take preventative measures to protect your plants3.
By adhering to these cultivation fundamentals, you can enjoy the serene beauty of Hostas in your garden, knowing that you’re providing them with
Seasonal Considerations
Understanding the seasonal needs of the Hosta plant is crucial for ensuring their vibrancy and long-term health. Here are key considerations to keep in mind:
- In summer, Hosta plants produce purple or white flowers on tall stems, thus, this is their blooming period3.
- As they enjoy cooler temperatures, ensure they have shade during the hotter parts of the day to protect their foliage.
- Regularly water your Hosta, particularly in dry spells, to maintain moisture since they flourish in well-hydrated soil1.
- Add mulch annually to help retain soil moisture and suppress weeds.
- Division of clumps may often be scheduled for early spring or late summer, to promote healthy growth for the next season3.
These simple steps will help your Hosta thrive throughout its growing season, showcasing its full ornamental potential.

Issues and Troubleshooting
- One common issue for Hosta plants is an infestation by slugs and snails. These pests are attracted to the tender leaves, leaving unsightly holes and damage.
- To combat these pests, natural deterrents such as eggshells or diatomaceous earth can be spread around the plants. Beer traps are also a popular method to lure and trap slugs and snails.
- If the Hosta leaves are browning or appear scorched, it may be due to too much sun exposure. Relocate the plants to a shadier spot or provide some artificial shade to protect them.
- Overcrowding can lead to poor air circulation and may result in fungal diseases. If the clumps are too dense, consider dividing the plants to encourage more airflow and reduce disease risk.
For best results, remain vigilant and provide regular care to maintain healthy Hosta plants.
History and Folklore
The Hosta plant, commonly known as plantain lily, weaves a rich tapestry through history and folklore. Despite the lack of folklore details in the original sources, these plants have deep cultural ties, especially in Asia where they originate. In Japan, Hosta varieties were not merely garden plants; they symbolized devotion and foresight, owing to their hardy nature and ability to thrive in shady environs. The Victorians later adopted them in England as a staple of elegant garden design, appreciating the textural and color variety of their foliage. Over time, Hosta plants have remained a firm favorite among gardeners for their lush leaves and graceful blooms.
References
1. “Growing Hostas: How to Plant and Care for Hosta Plants,” https://www.almanac.com/plant/hostas
2. “Hostas Benefits: An Easy Plant to Grow,” https://www.familyhandyman.com/article/hostas-benefits/
3. “Hosta: Plant, Grow and Care for Hostas,” https://www.gardenersworld.com/how-to/grow-plants/how-to-grow-hostas/
4. “How to Grow and Care for Hostas,” https://www.thespruce.com/how-to-plant-hostas-3963861
5. “Hostas care and growing guide: tips for these foliage plants,” https://www.homesandgardens.com/gardens/hostas-care-and-growing-guide
Image Credit: HansLinde
Image Credit: leoleobobeo
Image Credit: HansLinde
Nicolas Duval
Nicolas is a passionate advocate for nature and the art of wildcrafting. His dedication shines through in Wildcraftia, a website he meticulously crafted to serve as a haven for nature enthusiasts worldwide. Driven by a deep appreciation for nature’s connection to humanity, Nicolas embarked on his journey in 2011 with SmokableHerbs, a platform showcasing his love for nature’s bounty. Building upon this foundation, he established Smokably, a thriving online store offering premium herbs and blends to a global audience.