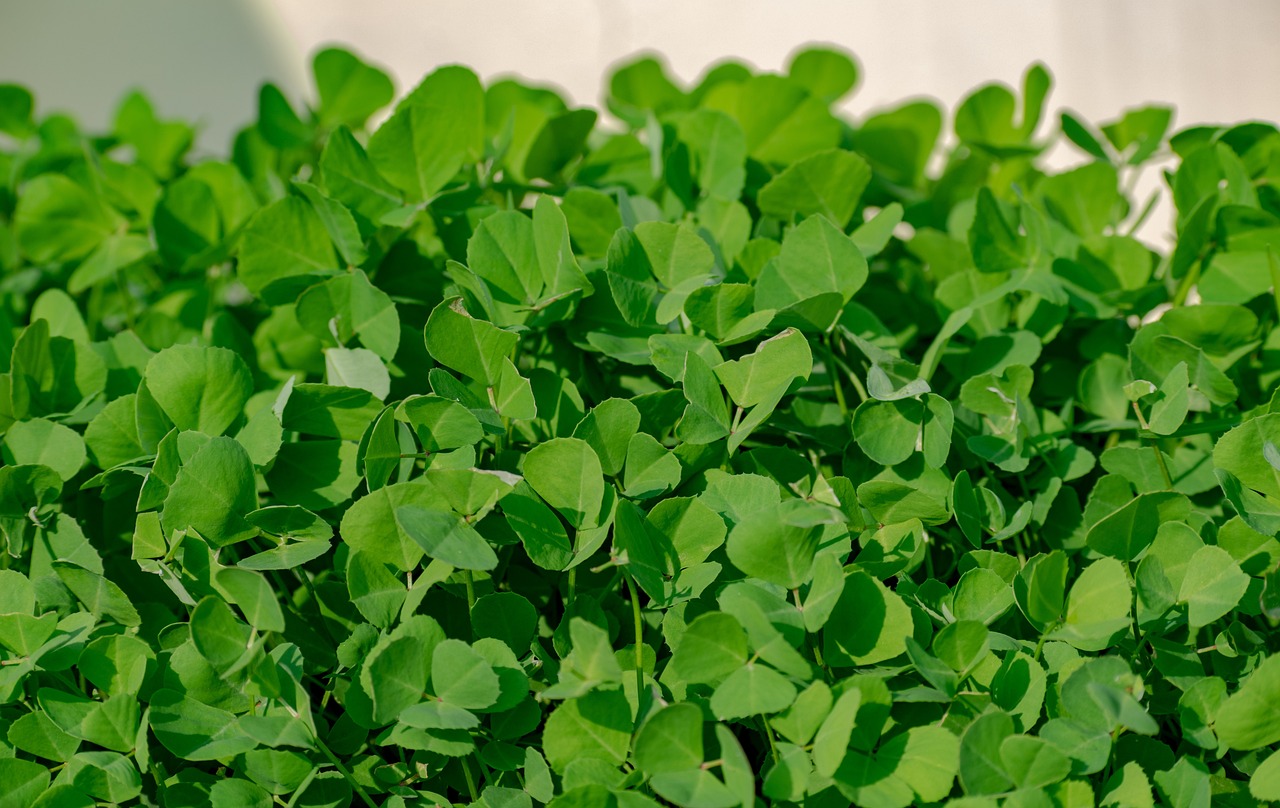
Fenugreek
Overview
Fenugreek, an annual plant of the legume family, is a versatile herb known for its delicate, clover-like leaves and strong aroma. Native to Mediterranean regions, it now flourishes across Asia and Africa. Celebrated for its culinary and medicinal applications, fenugreek adds a complex sweetness to dishes and offers several health benefits, often grown in a variety of climates with a preference for mild temperatures.

Characteristics
Known for its culinary and medicinal applications, the fenugreek plant thrives in warm temperatures, enriches the soil as a legume, and has a historical significance in traditional medicine.
Region
Dry regions around the Mediterranean, central and southeastern Europe, western Asia, India, and northern Africa.
Natural Habitat
Fenugreek is usually found in the wild in dry regions around the Mediterranean.
Cultivation
Prefers full sun, tolerates partial shade; requires well-drained, neutral to slightly acidic soil; moderate watering to avoid over-saturation.
Uses and Benefits
Fenugreek is a plant that’s as versatile as it is intriguing. In the kitchen, it’s a staple, especially in Indian cuisine, giving a distinct flavor to dishes that’s both sweet and nutty. But the benefits of this humble herb extend far beyond its culinary uses.
Medically, fenugreek has been a go-to remedy for digestive issues and is celebrated for its ability to potentially stabilize blood sugar levels3. Rich in fiber and other beneficial compounds, it has carved out a spot in traditional medicine, often consumed in the form of tea or supplements. Some of the key benefits of fenugreek include:
- Digestive Health: Fenugreek may help alleviate digestive problems like constipation and indigestion, thanks to its high fiber content.
- Blood Sugar Management: Studies suggest that fenugreek could help regulate blood sugar levels, making it a potential ally for those with diabetes or prediabetes.
- Lactation Support: Nursing mothers often turn to fenugreek to help increase breast milk production.
- Cholesterol Reduction: Some research indicates that fenugreek may help lower cholesterol levels, thus supporting heart health.
In addition to these health benefits, fenugreek can add a unique flavor to your cooking. Its seeds and leaves are used in various dishes, from curries and stews to bread and pickles. The seeds can be used whole or ground into a powder, while the leaves are often added to salads or cooked like spinach.
Whether you’re spicing up a meal or seeking a natural health boost, fenugreek has something to offer. This humble herb proves that nature’s gifts can be both delicious and beneficial.

Cultivation Tips
To cultivate fenugreek successfully, mimic conditions that are ideal for legumes. Full sun basks the plant in the energy it craves, but if that’s not possible, partial shade will suffice. Plant your seeds in soil that’s just right—not too acidic or alkaline—and ensure it’s well-draining to keep root rot at bay.
Sow fenugreek seeds in spring, post-frost, to avoid the chill. They should tuck into the earth about a quarter inch deep, with companions spaced 2-3 inches apart5. While managing your plant’s thirst, be cautious not to overwater to prevent unwelcome pests and diseases. With these tips in hand, watch your fenugreek flourish, becoming a fragrant addition to your culinary and medicinal herb gardens.
For optimal growth, consider the following cultivation tips:
- Choose a sunny location with well-draining soil
- Maintain soil pH between 6.0 and 7.0
- Sow seeds directly outdoors after the last frost
- Plant seeds 1/4 inch deep and 2-3 inches apart
- Water regularly, but avoid overwatering to prevent pest and disease issues
- Thin seedlings to about 4 inches apart when they reach 2 inches tall
- Mulch around plants to retain moisture and suppress weeds
- Harvest leaves as needed, and collect seeds when pods turn yellow and brittle
By following these cultivation practices, you’ll be on your way to enjoying a bountiful harvest of flavorful and nutritious fenugreek. This versatile herb is a fantastic addition to any home garden, providing both culinary and medicinal benefits.
Seasonal Considerations
To cultivate fenugreek successfully, mimic conditions that are ideal for legumes. Full sun basks the plant in the energy it craves, but if that’s not possible, partial shade will suffice. Plant your seeds in soil that’s just right—not too acidic or alkaline—and ensure it’s well-draining to keep root rot at bay.
Sow fenugreek seeds in spring, post-frost, to avoid the chill. They should tuck into the earth about a quarter inch deep, with companions spaced 2-3 inches apart5. While managing your plant’s thirst, be cautious not to overwater to prevent unwelcome pests and diseases. With these tips in hand, watch your fenugreek flourish, becoming a fragrant addition to your culinary and medicinal herb gardens.
Consider these seasonal tips for a bountiful fenugreek harvest:
- Spring is the ideal time to sow fenugreek seeds outdoors, once the threat of frost has passed.
- In regions with longer growing seasons, you can plant fenugreek in succession every 2-3 weeks for a continuous harvest.
- Fenugreek thrives in warm temperatures between 50-85°F (10-29°C).
- Protect young fenugreek plants from late spring frosts by covering them with row covers or cloches.
- As summer approaches, ensure your fenugreek receives adequate water, especially during dry spells.
- Harvest fenugreek leaves when the plant is 6-8 inches tall, typically 3-4 weeks after sowing.
- Collect fenugreek seeds in late summer or early fall when the pods turn yellow and begin to dry.
By understanding the seasonal needs of fenugreek, you can optimize your growing conditions and enjoy a flavorful, healthy harvest throughout the growing season.

Issues and Troubleshooting
When growing fenugreek, one of the most common challenges is dealing with pests like aphids. These tiny insects can quickly infest your plants and cause significant damage if left unchecked. To prevent this, it’s important to:
- Regularly inspect your fenugreek plants for signs of aphids, such as distorted leaves or sticky honeydew residue.
- Take action immediately if you spot any aphids by removing them manually or using an organic insecticide like neem oil.
- Encourage beneficial insects like ladybugs and lacewings, which are natural predators of aphids, to visit your garden.
Another issue to be aware of when growing fenugreek is root rot. This problem typically arises when the plants are over-watered or grown in poorly draining soil, leading to the roots sitting in excess moisture. To prevent root rot:
- Ensure your fenugreek is planted in well-draining soil that allows excess water to escape easily.
- Be mindful of your watering habits and avoid over-watering. Trigonella foenum-graecum prefers consistently moist soil but not soggy conditions.
- Consider using a moisture meter to help gauge when your plants need water and avoid guesswork.
By staying vigilant against pests and providing the right balance of water and well-draining soil, you can successfully grow healthy fenugreek plants. With proper care, these fragrant herbs will thrive, rewarding you with flavorful leaves, seeds, and pods that have a wide range of culinary and medicinal uses1.
History and Folklore
Fenugreek, or Trigonella foenum-graecum, is a plant deeply rooted in history and entwined with captivating folklore. This herb has woven its way through various cultures, often sprouting up in tales as a mystical panacea.
In ancient Egypt, fenugreek was highly regarded as an embalming herb, while in Greece, it was employed to promote healthy labor during childbirth. Throughout the Middle Ages, this enchanting herb was a key ingredient in potions believed to ward off evil spirits. It was also hung in homes as a symbol of prosperity and good fortune1.
In the realm of Ayurveda, India’s traditional system of medicine, fenugreek has long been revered for its remarkable healing properties. This ancient wisdom has contributed to the herb’s enduring presence as a cherished companion in the world of natural remedies.
From its mystical beginnings to its modern-day applications, fenugreek has stood the test of time, weaving its aromatic magic through the tapestry of human history.
References
1. How to Plant and Grow Fenugreek | Gardener’s Path, https://gardenerspath.com/plants/herbs/grow-fenugreek/
2. Fenugreek Plant Tips: Growing Methi – Epic Gardening, https://www.epicgardening.com/fenugreek-plant/
3. How to Plant, Grow, and Care for Fenugreek – Better Homes & Gardens, https://www.bhg.com/how-to-grow-fenugreek-7098344
4. Fenugreek | Description, Plant, Seeds, Uses, & Facts | Britannica, https://www.britannica.com/plant/fenugreek
5. Growing Fenugreek: Plant Varieties, How-to Guide … – MorningChores, https://morningchores.com/growing-fenugreek/
Image Credit: balouriarajesh
Image Credit: SandeepHanda
Image Credit: balouriarajesh
Nicolas Duval
Nicolas is a passionate advocate for nature and the art of wildcrafting. His dedication shines through in Wildcraftia, a website he meticulously crafted to serve as a haven for nature enthusiasts worldwide. Driven by a deep appreciation for nature’s connection to humanity, Nicolas embarked on his journey in 2011 with SmokableHerbs, a platform showcasing his love for nature’s bounty. Building upon this foundation, he established Smokably, a thriving online store offering premium herbs and blends to a global audience.